end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
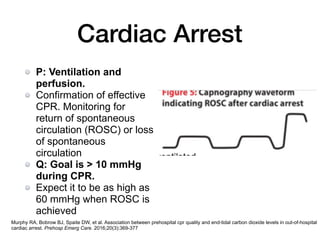
This is an example of capnography during CPR. End-Tidal CO2 in Cardiac Arrest.

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog
More Than Just a Number.

. Laboratory CPR studies indicate end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 during CPR is directly related to pulmonary blood flow and cardiac output and is therefore associated with survival 34712. The Journal of Emergency Medicine released an article traumatic brain injury careOriginal Article. End-Tidal CO2 as a Predictor of Cardiac Arrest Survival.
To describe onscene times for outofhospital cardiac arrests OHCA transferred to hospital the number of these that were extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation ECPR eligible and. End Tidal CO 2 Is a Quantitative Measure of Cardiac Arrest. In one of largest studies to date of prehospital capnography in cardiac arrest an initial EtCO2 10 mmHg 13 kPa.
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST. Predicting likelihood of return of. The initial values of PetCO2 were significantly higher in the group with asphyxial cardiac arrest 674 422 kilopascals kPa versus 451 247 kPa.
In one of largest studies to date of prehospital capnography in cardiac arrest an initial EtCO2 10 mmHg 13 kPa was. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a. Kolar M Krizmaric M Klemen P Grmec S.
Partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide successful predicts cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the field. These values are approximately 14 the normal EtCO2 35-45 mm Hg and ideal CPR will provide at least 14 of cardiac output. MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr.
End tidal carbon dioxide CO2 correlates with cardiac output during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in cardiac arrest patients. In the group with asphyxial. BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end.
Geoff Murphy from Master Your Medics provides a refresher training video on end. Because impaired circulation during arrest causes CO2 to build up in the bloodstream the initial ETCO2 reading may initially be higher than the normal 35-45 mm Hg. Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare.
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationwhen Is Capnography Useful In The Ed Part Ii Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

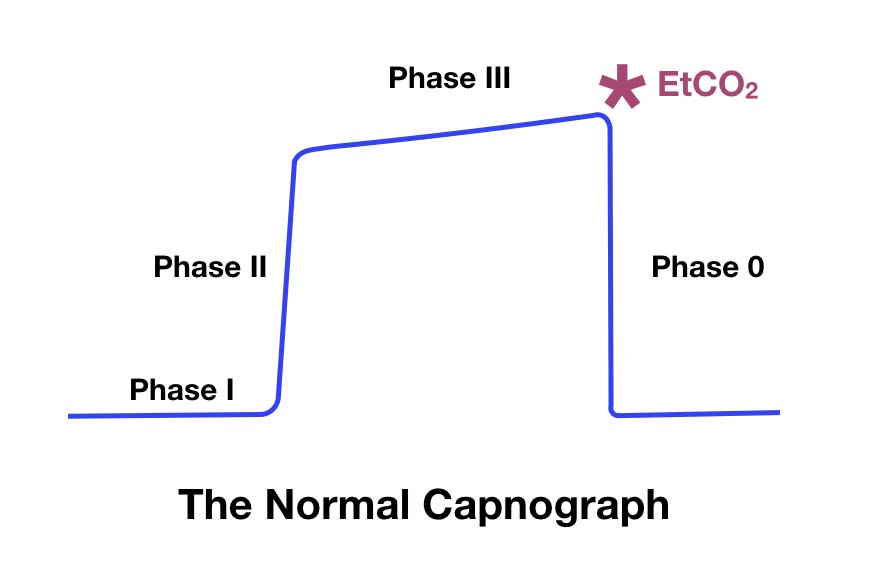
3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationwhen Is Capnography Useful In The Ed Part I Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide And Outcome Of Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Nejm

Intraoperative Cardiac Arrest Anesthesiology Clinics

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog

What S In A Wave Form Utilizing End Tidal Capnography For More Than Intubation Confirmation Criticalcarenow

Continuous Waveform Capnography A Crucial Tool For Ed Clinicians American Nurse

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Capnography In Cardiac Arrest Youtube
Be All End Tidal The Expanding Role Of Capnography In Prehospital Care Ems Med

Abstract 223 End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels Predict Cardiac Arrest Circulation

Waveform Capnography For Monitoring Ventilation During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation The Problem Of Chest Compression Artifact Intechopen